The Directorate-General for Public Health, through the Food Safety Service, reminds that preparing food to be consumed outdoors during the summer months can carry the risk of food poisoning if some basic hygiene rules are not followed.
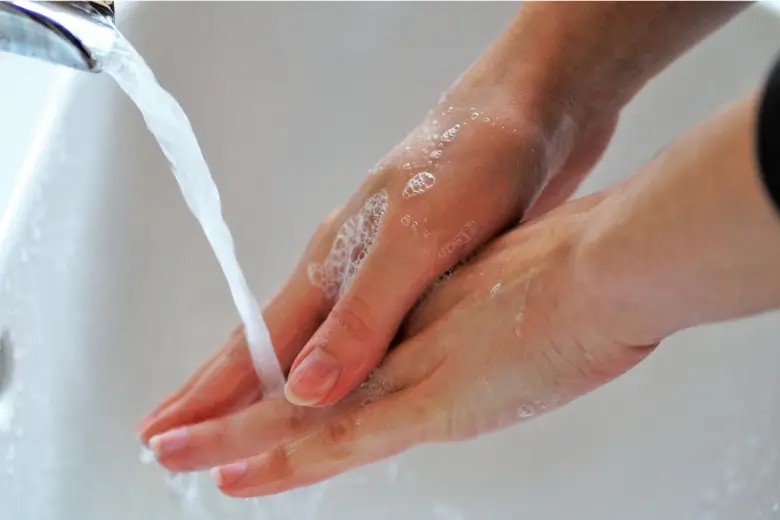

It is essential to wash your hands before and after handling food. Photo: CAIB.
The most common food poisonings are salmonellosis, listeriosis, E. coli, or campylobacteriosis, which usually present symptoms such as gastroenteritis, fever, and vomiting.
Tips to avoid food poisoning in the summer
- It is essential to wash your hands before and after handling food.
- Disinfect fruits and vegetables that will not be cooked, using a few drops of bleach suitable for this purpose.
- If you prepare salads, it is important to mix the ingredients just before eating to avoid cross-contamination.
- Keep raw and cooked foods separate.
- Meat should be cooked thoroughly.
- Avoid, as much as possible, foods prepared with raw egg.
- Omelettes, for example, should be well-cooked and kept in portable coolers until consumption. During their preparation, it is recommended to:
- Do not crack the eggs on the same plate where they will be beaten.
- Do not use the shell to separate the yolk from the white.
- Do not place the omelette on the same plate used to flip it in the pan.
- During transportation, it is advisable not to leave food in the car for a long time to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Do not defrost food at room temperature; it is safer to do so in the refrigerator to prevent the proliferation of bacteria.




Leave A Comment